You've followed Prerequisites and got everything you need. Now you have to prepare your device for flashing.
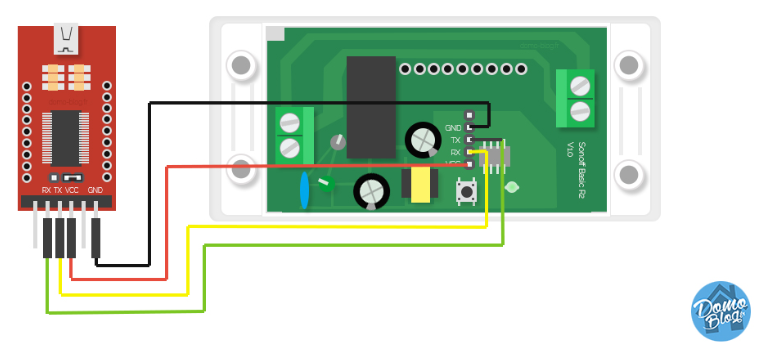
We need to connect to the serial programming interface of the ESP8266 chip. This is done by connecting our serial-to-USB converter TX and RX pins to the ESP8266 RX and TX pins and powering the chip with the 3.3V and GND pins.
In most cases those pins are available on the PCB in the form of pin holes or solder pads but pin headers or jumper wires need to be soldered or otherwise applied. In some cases you will need to solder wires directly on the chip's pins which requires some experience and good soldering equipment.
⚠️ WARNING BEFORE PROCEEDING ⚠️
DO NOT CONNECT DEVICES TO MAINS POWER WHILE THE COVER IS OPEN AND CIRCUIT BOARD IS EXPOSED!!!
NEVER TRY TO FLASH WHILE YOUR DEVICE IS CONNECTED TO MAINS POWER!!!

YOU CAN BE ELECTROCUTED IF YOU DON'T KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING!
If you are not careful, your own health will be in danger. Shorting your serial interface with mains AC power will fry your device and serial adapter and will also harm or destroy your computer. It is important to always have all mains power cables disconnected from the device while being connected via serial or even while the case of the device is opened.
Serial Connection
Each device has its pins labelled differently. If the labelling isn't visible on the PCB please refer to the devices flashing guide or search the Internet for correct pin locations. Device specific instructions and restrictions are documented in the Tasmota Device Templates Repository
When you have identified pins on your device, connect wires according to the table:
| Serial adapter | ESP8266 device |
|---|---|
| 3V3 | 3V3 or VCC |
| TX | RX |
| RX | TX |
| GND | GND |
Note that TX from your adapter goes to RX on the ESP8266 device and RX from adapter goes to TX on the device!
Putting the Device into Programming Mode
 ESP8266 needs to be put into Programming Mode before the firmware can be uploaded. This is done by pulling the GPIO0 pin to GND while the chip is booting.
ESP8266 needs to be put into Programming Mode before the firmware can be uploaded. This is done by pulling the GPIO0 pin to GND while the chip is booting.
On most devices the installed control button is connected to GPIO0 and GND, making entering Programming Mode very easy. On others you will need to bridge the pins on the PCB or directly on the chip with a jumper wire. Device specific instructions are documented in Tasmota Device Templates Repository.
To put the ESP8266 into Programming Mode:
- Disconnect serial-to-USB adapter and power
- Bridge GPIO0 and GND (by pressing the on-board button or connection with a wire)
- Connect the serial-to-USB adapter to your computer
- After a few seconds disconnect GPIO0 from GND (release button or remove the wire connection). On devices that do not provide the GPIO0 connected button, it may be easier to leave the wired bridge in place throughout the entire flashing process (erase & upload). Doing so will not create any problems. After the firmware is uploaded successfully, remove the bridge. This allows the device to boot normally.
You can test whether your device is in Programming Mode by attempting to read information from the ESP82xx chip. This requires esptool.py. Instructions on installing and using esptool are provided in the Flashing article. For example (COM5 will be your COM port):
esptool.py -p COM5 read_mac(It should read the MAC address. It may fail afterwards during Uploading and running a "stub". This is normal.)esptool.py -p COM5 flash_id
If everything went well, you are now in Programming Mode and ready to continue with flashing. If the flashing process is unable to start, disconnect the device and retry the steps.
Common Mistakes
- Wire connections and solder joints - Double check all connections and also check for solder overflow.
- Use a USB data cable - Some USB cables are for charging only and do not connect the data lines needed to load the firmware onto the device.
- Insufficient power delivered over the serial-to-USB adapter. This leads to flashing failures or corrupted flash altogether. Supply more power with a separate 3.3V power supply or get an adapter with a better power supply. Be sure all DC voltages use the same GND reference.
- Recheck your serial-to-USB adapter so to ensure that it supplies 3.3V voltage and NOT 5V. 5V will damage the ESP chip!
- Releasing GPIO0 button/wire before booting is finished - It is safe to leave GPIO0 connected to GND during the entire programming process (erase & upload). Just be sure to remove the GPIO0 to GND bridge before booting the device for regular operation.
- Make sure that the RX pin is connected to the TX pin between the serial adapter and your ESP device, and vice versa.
- Erase the flash memory first and cycle power afterwards before uploading the Tasmota firmware binary. Not erasing can leave behind remnants of the previous flash contents which can interfere with the new firmware operation.
Wiki has moved to link on the left.